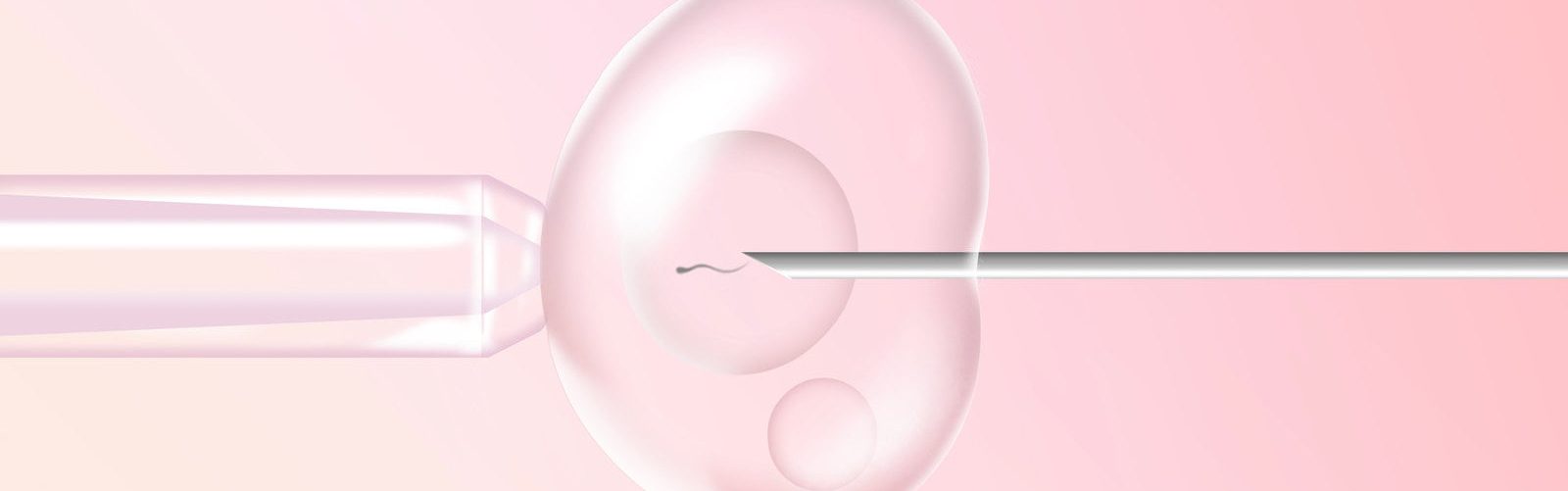
How to do In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)?
Initially, the egg is taken from inside the ovaries and inoculated with male sperm in a laboratory setting. The embryos are then cultured for 2-5 days and finally transferred to the uterus
The patient should not be exposed to stress in the coming days after performing all IVF procedures.
For whom is IVF infertility treatment suitable?
This method is offered as a main treatment for infertility in women over 40 years.
Damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes makes it difficult to fertilize an egg or transfer the fetus to the uterus.
Ovulation Disorders: If ovulation is low, fewer eggs are available for fertilization.
Endometriosis: Occurs when uterine tissue (endometrium) begins to grow outside the uterus, often affecting the function of the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
Uterine fibroids: Benign tumors in the wall of the uterus and are common in women aged 30-40. Fibroids can interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg.
History of sterilization or removal of the fallopian tube: A type of sterilization in which the fallopian tubes are cut or blocked to prevent a permanent pregnancy. Poor motility or abnormal sperm size and shape can make it difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg.
Infertility of unknown cause: Unknown infertility means that despite assessing the common causes of infertility, no cause has been found.
Checking for a genetic disorder: If you or your partner are at risk for your child having a genetic disorder, you may be a candidate for a preimplantation genetic test. The procedure involves IVF. In this method, after the eggs are fertilized and removed from the uterus, they are sent to a laboratory for genetic problems, although not all genetic problems can be found. Fetuses that do not have specific problems can be transferred to the uterus.
Maintaining fertility if you have cancer: Treating cancer – such as radiation or chemotherapy – can damage fertility. IVF is a way to maintain fertility. In these women, healthy, mature eggs can be removed from the ovaries and frozen. These eggs are used for fertilization after cancer treatment.
Women who have uterine dysfunction or are at high risk for pregnancy may choose to use IVF to conceive. In this case, the female’s eggs are fertilized with sperm, but the resulting fetus is placed in another person’s uterus and transported.
Despite the different methods of infertility treatment, all couples can have their own child. The only thing is that you have to be very careful in choosing an infertility specialist to get the best results from your treatment.
How long does IVF treatment take?
Some drugs must also be taken after the transfer of the fetus. The hormone progesterone strengthens the layers of the uterus and reduces uterine contractions. Therefore, this hormone must be taken by a woman by injection or vaginal suppository. After two weeks, the person should go to the lab and the amount of HCG hormone in the patient’s blood is measured, and if this hormone is increased, it can be a sign of successful IVF.
If IVF leads to pregnancy, the pregnancy is like a normal pregnancy and the mother should no longer have any special worries. And your delivery is related.
What is the chance of pregnancy in IVF?
Based on references and medical articles, the fertility rate with ivf is maximum 35-40%.
The steps of IVF are:
The ovary is first stimulated for ovulation (first about 2 weeks of fertility medication is prescribed). Ovulation (along with ultrasound and laparoscopy) is fertilized in a container of the obtained egg with sperm. Finally, the embryo is transferred to the uterus for implantation. The patient can be discharged in a few hours.
Hormonal tests are performed to check for pregnancy hormone levels two weeks after fetal transfer.
Because multiple embryos are formed, these extra embryos may be frozen for use in subsequent IVF cycles.
Complications of IVF:
Breast tenderness, constipation, bloating, mild abdominal cramps and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, etc., some of which are related to the drugs used in this process, and other side effects can increase the chances of multiple births, increase the risk of childbirth. Premature, low birth weight and so on.
Post-IVF care:
After the transfer of the fetus, it is better for the mother to rest for 24 hours and then start daily activities. Do not swim or take a bath for 48 hours. Do heavy work, lifting heavy objects, intense physical activity. And exercise is not recommended until the pregnancy is stable.
Be sure to see your doctor if you notice bleeding or moderate or severe pain
Islamic and Shiite views on IVF, which is a type of infertility treatment:
According to Islam and Shiite religion, if a husband’s sperm and a woman’s egg are mixed outside the uterus, that is, in an artificial system, and a sperm is coagulated, it is permissible to insert this sperm (at any stage of the fetus that has reached) into the spouse’s uterus.
Determining sex before fertilization in PGD &IUI
Scientific methods for determining sex before pregnancy are based on medical science and have a high success rate for determining sex.
The rate of response depends on the method chosen, the infertility center or fertility center where it is performed, and the skill of the person performing it.
This method includes:
Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) during IVF: This method was first developed to help couples who were sexually transmitted through sexually transmitted diseases, which was used at the same time as in vitro fertilization (IVF), but later on. The method was also used to determine sex before pregnancy.
The steps to perform PGD are:
Step 1. Perform in vitro fertilization (IVF) to collect fertile eggs
Stage 2. Embryo development for several days in the laboratory (for two to three days until the cells divide and the fertilized egg forms about eight cells)
Step 3. Harvest one or two cells from the dividing egg by an embryologist
Step 4. Examine the fetal chromosomes selected to examine for specific genetic problems or to determine the sex of the fetus
Step 5. One, two or three fetuses of the desired sex are transferred to the uterus for growth.
Step 6. The rest of the embryos are frozen for later use, or used for further research, or destroyed.
Sperm sorting: This technique involves separating sperm containing the Y chromosome from sperm containing the X chromosome in the laboratory and transferring the sex of the desired sex into the uterus through intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization.